
The following factors can contribute to the development of arthrosis of the knee joint:
- excessive physical activity that does not meet the requirements of age, leading to damage to the joints;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- suffered injuries in the knee joint area - knee dislocation, fractures, rupture and torn ligaments, damage to the meniscus body, severe falls on the knee, bruises;
- increased body mass index, which leads to increased pressure on the joints, rupture of the meniscus;
- descent;
- arthritis or other joint diseases (inflammation can cause the appearance of edema or accumulation of large amounts of synovial fluid in the joints, provoking the destruction of cartilage tissue);
- metabolic disorders leading to excretion of calcium from the body;
- diabetes mellitus of any kind, hormonal disorders and other pathologies of the endocrine system;
- chronic or chronic diseases of an inflammatory and infectious nature;
- violation of blood flow;
- lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid, gouty and psoriatic pathology, ankylosing spondylitis;
- flat feet, as the center of gravity shifts and the load on the joints increases;
- nerve load and stressful situations.
Why arthrosis of the knee joint occurs
Often, people themselves are the cause of the development of diseases that are difficult to control. Often, when pain in the knee joint appears, people ignore the painful sensation, preferring to go to the doctor to use any medication that only covers the pain.
After a few years, you still need to consult a specialist, because with such a diagnosis, the drugs themselves will not give results. However, the severity of arthrosis will be at least average. Here, ointments, intra-articular administration of hyaluronic acid and preventive physical education are no longer sufficient, as can be done in the early stages of the disease course. Most likely, it is necessary to act radically, including sometimes by using surgical intervention.
Symptoms and diagnosis of knee joint arthrosis
The disease can be distinguished by the following features:
- Pain syndrome. Painful sensations usually occur suddenly, but often with physical effort, even a little. Pain can be of a different nature. At first, this will be a weak lumbago (unfortunately, very few people pay attention to them). Mild pain that occurs only periodically can last for months, or even years, until the disease progresses to a more severe stage.
- Significant knee deformity. The same symptoms are typical for the next stage. And at the beginning of the development of arthrosis, the knee swells and swells slightly.
- Appearance of solid formations in the posterior wall of the knee joint. Accumulation of large amounts of joint fluid in the cavity of the Baker cyst or in the joint itself.
- Crispy sharp joints, which are accompanied by pain.
- Decreased joint mobility. This is especially noticeable in the last stages of arthrosis. In this case, flexion and extension of the knee cause severe pain, and in the last stage, movement becomes almost impossible.
REFERENCE! In patients with arthrosis, the gait changes: it is characterized by drooping legs and lameness.
Pathogenesis of arthrosis of the knee joint
Specialists distinguish between primary and secondary arthrosis.
Primary arthrosis of the knee joint
For primary gonarthrosis, the following processes are characteristic:
- Articular cartilage is capable of constantly deteriorating and at the same time being rapidly renewed. Under normal circumstances, these two processes should balance each other. With the passage of age, cartilage destruction occurs at a similar rate, but recovery is slow. A person’s mass plays an important role here. Indeed, if a person’s mass is 70 kg, then in 10 steps on one leg he will move 700 kg, and a person weighing 120 kg will move as much as 1200 kg, which will be a significant load on the joints and cartilage, which will wear out fasterbecause of this.
- It is important to remember: joints consume useful elements only when moving. An inactive lifestyle leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes, which is why the necessary nutrients do not reach their destination.
- The likelihood of developing gonarthrosis is increased in people whose parents suffer from the disease.
Secondary arthrosis of the knee joint
It develops for the following reasons:
- Multiple injuries. In a person at any age, they will cause excessive pressure on the cartilage. When any bone is covered with broken cartilage, a deviation, called a "step", appears. In this area, now, with any movement, the joint will disappear, leading to arthrosis.
- Development of rheumatoid arthritis, Koenig's disease, appearance of purulent inflammation in the joint area.
- Vascular dysfunction.
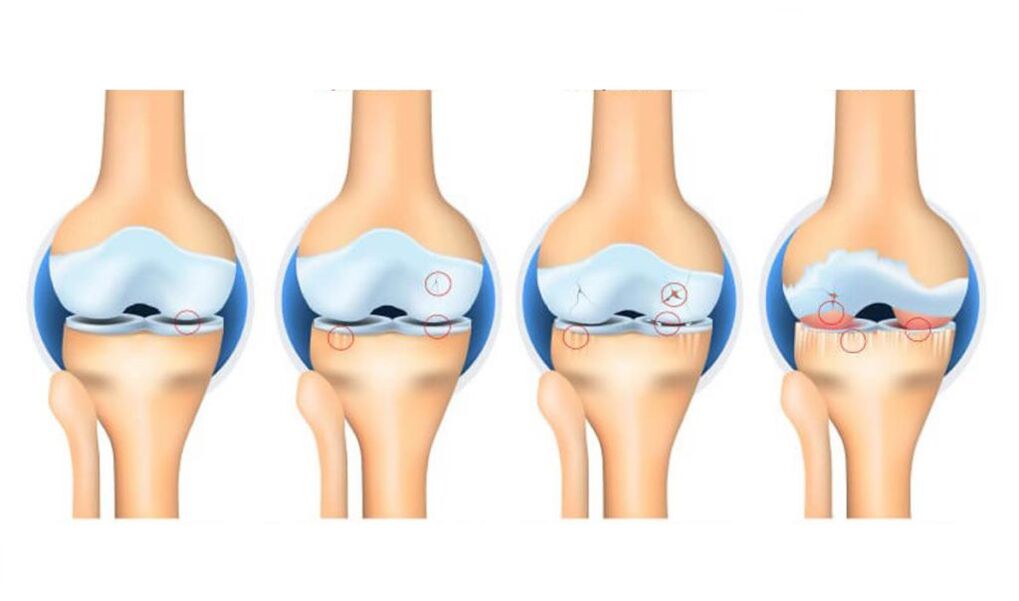
Classification and stage of development of knee joint arthrosis
Orthopedists divide gonarthrosis into stages, on which further treatment of the disease depends. Of course, the course of treatment will also depend on other factors, for example, the causes of development, localization and nature of the arthrosis.
IMPORTANT! Qualitative treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor after a complete study of the picture of the disease. Self -administered therapy can only worsen the health condition.
The main classification divides gonarthrosis into four stages of development:
- Early stage. At this stage, the disease is emerging. External symptoms are almost insignificant or completely absent, the shape of the joints is in a satisfactory condition. Symptoms include only mild or severe discomfort in the knee after a long walk, as well as vigorous physical exercise. The x-ray examination will contain little information: the x-ray may show only a slight narrowing of the joint space. Unfortunately, at this stage, a person does not seek medical help because of insignificant symptoms.
- The second stage is characterized by a significant pain syndrome, especially when walking and climbing stairs, as well as at night. The severity of the pain decreases during rest. Joint movement becomes difficult. There is a squeak or squeak of the knee while walking. On X-ray, the narrowing of the joint space becomes noticeable, as well as osteophytes. The patient began to drown.
- Once the arthrosis has passed to the third stage, the pain syndrome will be felt continuously, even without movement. The process of deformation and degeneration goes through an irreversible stage. Joint distortion becomes significant, the distance between articular surfaces is significantly reduced, many osteophytes increase in size. The painful sensation now bothers the patient even in a state of complete rest. A person becomes dependent on external support (walkers, crutches) and needs help from others. Conservative treatment at this stage is less effective.
- The fourth stage is characterized by persistent debilitating pain. Osteophytic growth increases in number and size, cartilage is completely destroyed, joint space is almost undetected or completely absent, bone is severely deformed. Even weak movements become torture for the patient. At this stage of gonarthrosis, the patient is recognized as disabled. In the absence of surgery, the disease can lead to disability.
Complications of arthrosis of the knee joint
Advanced arthrosis can cause dislocation and subluxation of the knee joint. With dislocation, the femoral epiphysis extends completely beyond the joint, as movement within the joint becomes impossible, and the axis of the foot shifts much to the side. Fortunately, negative variants of the development of this disease are relatively rare.
Subluxation is more common. They are characterized by partial displacement of the joints relative to each other and slight deviation of the tibial axis. In this case, subluxations are accompanied by severe pain and joint dysfunction.
Neglect of this disease can lead to complete loss of lower limb function.
ATTENTION! The habit of enduring leg pain sometimes leads to deformation of the intervertebral disc and the appearance of a hernia.
Consequences of neglected gonarthrosis
Advanced stages of gonarthrosis are almost always characterized by the following adverse symptoms:
- pain all the time, which cannot be saved by painkillers;
- loss of support for the limbs (impossible to stand on a sore leg or at least to lean);
- articular block immobilization;
- significant bone curvature around the knee;
- severe swelling around the affected area.
Methods for the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
The treatment prescribed depends on the stage of development of the disease. There are several therapy options.
Hormones
These medications are prescribed for severe exacerbation, accompanied by synovitis and severe pain. Usually hormones are given by injection. The following medications are most commonly used:
- Flosteron;
- Diprosfan;
- Hydrocortisone.
The course of treatment with hormones is usually short; injections are performed only during periods of severe deterioration. Hormones are administered at an average frequency of once every 10 days.
Chondroprotectors
Chondroprotectors are prescribed in the early stages of disease development. This therapy is currently considered the most effective and safest: there are almost no contraindications, and side effects appear in the rarest of cases.
These drugs aim to restore cartilage, improve metabolic processes, nourish cartilage tissue and protect it from further destruction. But in the last stages of arthrosis, chondroprotectors are also powerless.
This group of drugs is produced in the form of injections, ointments, gels, tablets.
Vasodilator drugs
These funds are needed to eliminate the spasm of small vessels, improve blood circulation and supply of nutrients to the affected joint area. Prescribed to take vasodilators along with chondroprotectors.
If articular fluid does not accumulate during gonarthrosis (no synovitis), it is recommended to use a warming ointment.
Hyaluronic acid
In another way, this device is called an intra-articular fluid prosthesis, because the acid composition is similar in composition to the intra-articular fluid. When acid is injected into a joint, it forms a film that prevents strong cartilage friction during movement, affects the extracellular matrix, enhances metabolic processes in the joint, and even triggers the production of hyaluronic acid itself in the joint - i. e. restores joint function to normal, stopping the pathological process that destroys cartilage. . . .
Acid treatment is prescribed only when exacerbation - synovitis is eliminated.
Physiotherapy
A course of physiotherapy training will bring positive results only if it is prescribed by a doctor after a complete review of medical history, and all training is carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
Medications alone often lead to deterioration of joint conditions. Exercise therapy is prescribed for the following purposes:
- slows the development of stiffness;
- prevention of further destruction of cartilage tissue;
- elimination of muscle spasms, which lead to pain.
Physiotherapy
As adjunctive therapy, various procedures can be prescribed: electrophoresis, acupuncture, laser therapy, UHF, as well as diadynamic currents. A local massage will also give good results.
Physiotherapy aims to reduce the severity of pain, eliminate inflammation, normalize metabolic processes in the affected joint and restore its normal function.
IMPORTANT! It is important for patients to monitor their diet and avoid strenuous physical activity.
Prediction. Prophylaxis
With the advanced stages of the disease, the prognosis is disappointing. Therefore, it is recommended that if even minor arthrosis symptoms occur, see a doctor for advice.
People at risk (the elderly, athletes, as well as overweight people) must follow their doctor's recommendations and adhere to the following rules:
- Eat right and control your weight. Follow a weight loss diet as needed.
- Reduce the load on the joints while playing sports, constantly monitor them.
- Treat infectious diseases in a timely manner, preventing their transition to the chronic stage.
- Get adequate rest, avoid stressful situations if possible.
- Improves the protective function of the body (regularly take vitamins, be patient).
- Avoid hypothermia of the body, especially the lower legs.

















































